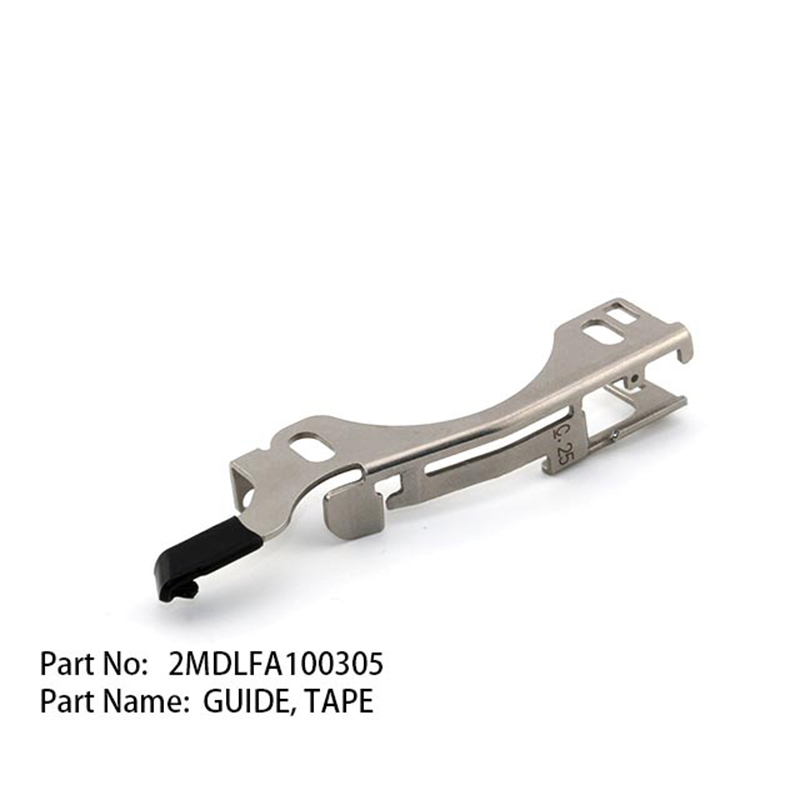
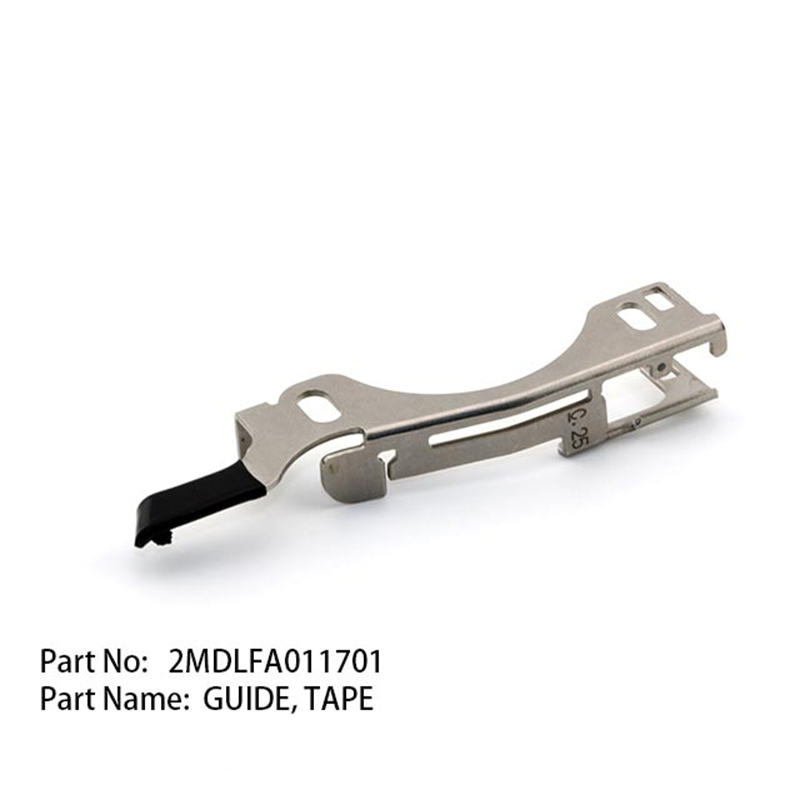
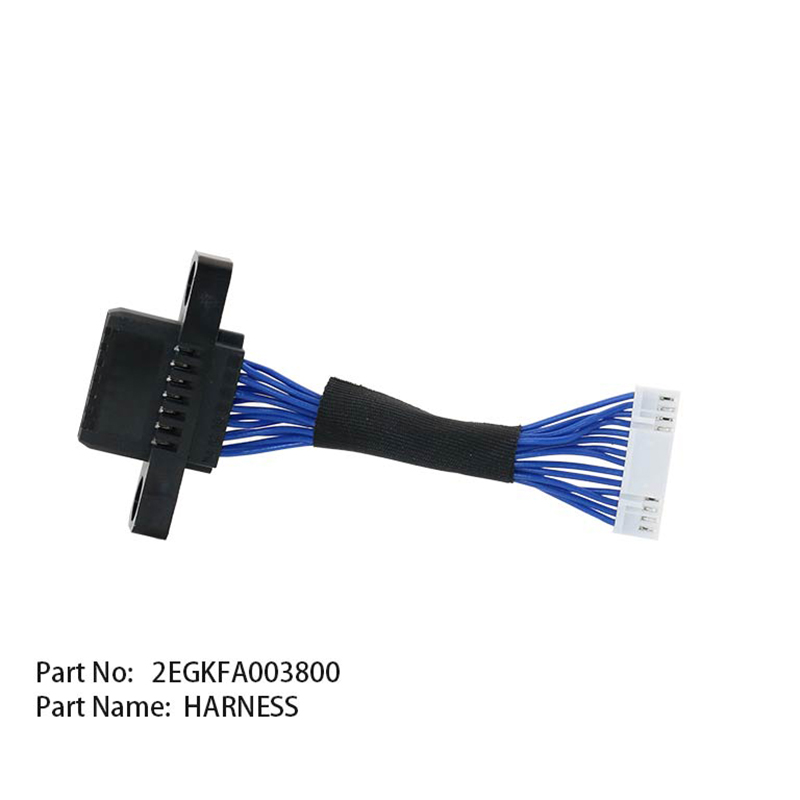
What factors need to be considered when customizing a special feeder for the vibratory feeder in an SMT pick-and-place machine?
Release Time : 2025-12-31
In SMT pick-and-place machine feeders, the customization of special feeders for vibratory feeders requires a systematic design encompassing core dimensions such as component characteristics, equipment compatibility, feeding efficiency, structural stability, ease of maintenance, environmental adaptability, and cost optimization. This ensures that they meet the production demands for high precision, high efficiency, and high stability.
Component characteristics are the primary consideration in customizing special feeders for vibratory feeders. The size, shape, weight, and surface characteristics of different components directly affect the choice of feeding method. For example, micro-components (such as 0201 resistors and capacitors) require precise alignment via micro-vibration tracks to prevent splashing due to excessive inertia; while irregularly shaped components (such as irregular ICs and connectors) require dedicated guide grooves or vacuum adsorption structures to ensure their pin orientation matches the pick-and-place machine nozzles. Furthermore, the electrostatic sensitivity of components necessitates the use of anti-static materials (such as conductive plastics and carbon fiber reinforced composites) to reduce the risk of adsorption and prevent component adhesion or feeder malfunction due to static electricity buildup.
Equipment compatibility is a crucial aspect of the customization process. The feeder of the vibratory feeder must be highly compatible with the mechanical interface, electrical protocol, and feeding platform of the pick-and-place machine. For example, for Panasonic NPM series pick-and-place machines, the feeder's positioning latches must match the feeder's mechanical locking mechanism to prevent feeding deviations due to installation errors. Simultaneously, its communication module must support the RS-485 protocol to achieve real-time data interaction with the equipment control system. For high-speed pick-and-place machines, the feeder's feeding frequency must be synchronized with the equipment's placement speed to avoid material rejection or machine downtime due to feeding lag.
Feeding efficiency and stability are core indicators for evaluating feeder performance. The vibration frequency, amplitude, and track design of the vibratory feeder need to be optimized through simulation to ensure that components are arranged at a uniform speed on the track, avoiding component accumulation due to excessive vibration or jamming due to insufficient vibration. For example, for high-density packaged components (such as QFN and BGA), a multi-channel parallel feeding structure is required, with independent vibration sources controlling the feeding rhythm of each channel to increase the component supply per unit time. Furthermore, the feeder's belt tension control system must possess adaptive adjustment capabilities, dynamically adjusting tension based on component dimensions to prevent component deformation due to excessive tension or belt slack due to insufficient tension.
Structural stability and durability directly impact the feeder's lifespan and maintenance costs. The vibratory feeder body must be made of high-strength aluminum alloy or stainless steel, with precision machining ensuring that the clearance between components is controlled at the micrometer level to prevent structural loosening due to long-term vibration. Key components (such as the vibratory motor and spring plates) must be made of wear-resistant materials, and their stress distribution must be optimized through finite element analysis to extend their service life. For example, one brand of feeder, by using a carbon fiber composite vibratory feeder, has increased the feeder's lifespan from 3 years with traditional metal materials to over 5 years, while simultaneously reducing vibration noise.
Maintenance convenience is crucial for improving production efficiency. The feeder must be designed with a modular structure for easy disassembly and replacement of vulnerable parts (such as the vibratory motor and guide rails). For example, using quick-release positioning pins and spring clips allows maintenance personnel to install and debug the feeder without tools, reducing maintenance time from 30 minutes in the traditional solution to less than 5 minutes. Furthermore, the feeder's cleaning design must consider a seamless structure to prevent feeding malfunctions caused by dust accumulation.
Environmental adaptability is crucial for ensuring stable feeder operation. For high-temperature and high-humidity environments, the feeder must employ a sealed structure design to prevent moisture intrusion and short circuits in electrical components; simultaneously, its surface must undergo anti-corrosion treatment (such as nickel plating and conformal coating) to enhance corrosion resistance. For cleanroom environments, the feeder must reduce particulate matter generation through dust-free design (such as enclosed tracks and oil-free lubricated bearings) to avoid contaminating the production environment.
Cost optimization must be achieved while meeting performance requirements. Manufacturing costs can be reduced through material substitution (such as replacing some metal parts with engineering plastics), structural simplification (such as merging multi-functional modules), and standardized design (such as unified interface specifications). For example, one company reduced the number of parts by integrating the feeder's vibration motor with the track guide, resulting in a 15% reduction in unit cost while improving assembly efficiency.